Generative-Vs-Discriminative-Models
In this blog post we will be learning about Generative and Discriminiative models. Suppose that we have one model which can learn things in-depth and thoroughly and we have another model which can learn to identify only the differences between the things it sees.
For example suppose we have model A which can learn features of fruits such as color, texture, shape etc and other model B learns only the features which help to easily classify them like their color. Model A is a generative model and model B is a discriminative model.
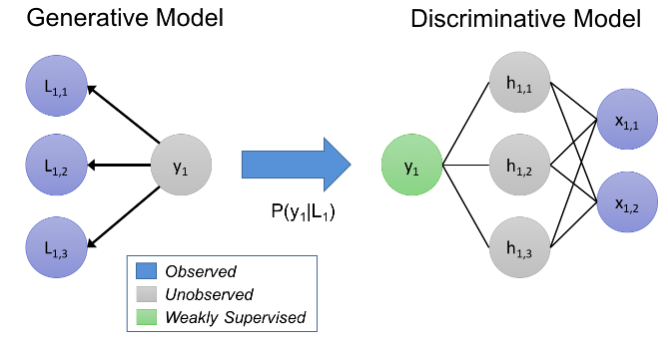
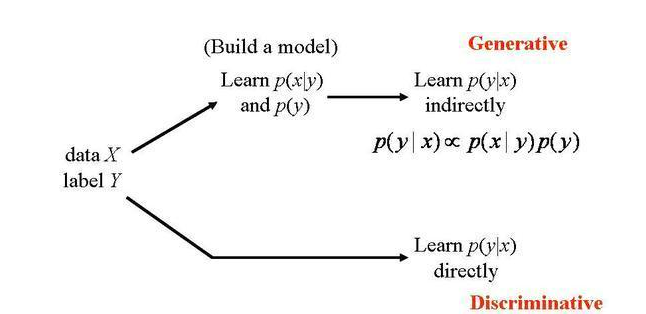
The geneartive models learn the joint probability distribution p(x,y) and a discriminative model basically learns the conditional probability distribution p(y|x). A generative algorithm models how the data was generated in order to categorize a signal whereas a discriminative model does not care about how the data was generated, it simply categorizes a given signal.
Generative Models
In technical terms, a Generative model learns the joint probability distribution p(x,y). For example, if you have input data x and you want to classify it into y labels. Since generative models model each class separately they can be trained on an individual class basis. Some of the examples include Naïve Bayes, Hidden Markov Models (HMM), Markov random fields.
Discriminative models
A Discriminative model learns the conditional probability distribution p(x|y) using Bayes theorem. The main aim of dicriminative models is to distinguish between classes, it needs to be trained on a single traning set with examples of all of them. Some of the discriminative models include Conditional Random Fields (CRF)s, Logistic regression, Traditional neural networks and Nearest neighbour. These models are more complex than generative models.
Discriminative machine learning is training a model to distinguish the correct output among possible output choices, given something about the data. This is typically done by learning model parameters that maximize the conditional probability P(Y/X).
Advantages and Disadvantages of Generative and Discriminative Models
Generative models
- They are computationally very expensive.
- They are good at unsupervised machine learning.
Discriminative models
- They are computationally less expensive.
- Very good at supervised machine learning.
We can also conclude that the lower layers of deep neural networks can be called as generative and the upper layers often as discriminative. Generative models often outperform discriminative models on smaller datasets because their generative assumptions place some non-restriction on your model that prevent overfitting. For example, if we compare Naive Bayes vs. Logistic Regression, the Naive Bayes assumption is of course rarely satisfied, so logistic regression will tend to outperform Naive Bayes as your dataset grows (since it can capture dependencies that Naive Bayes can’t). But we have only a small data set, logistic regression may pick up on false patterns that don’t really exist, so the Naive Bayes acts as a kind of regularizer on our model that prevents overfitting.