Learn CUDA Programming using Google Colab
In this blog post we will learn about CUDA programming, difference between C and CUDA programming and how it is efficient. Generally these days laptop and computers have shared CPUs and GPUs in-built, but we will learn how to use Google Colabs for CUDA programming.
What is CUDA?
CUDA is NVIDIA’s parallel computing architecture that enables increase in computing performance by utilizing the power of GPU (Graphical Processing Unit). CUDA provides C/C++ language extension for programming and managing GPUs.
Structure of CUDA programming
- Both CPUs and GPUs are used for computations.
- CPU systems are referred as host and GPU systems as device.
- Both CPU and GPU have completely separate memory space.
- Serial workload is performed on CPUs and parallel computations on GPUs.
Difference between CUDA and C Programming
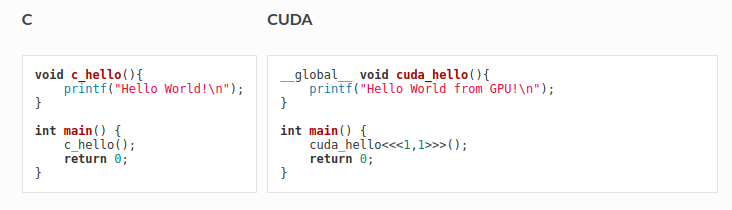
There are various differences between CUDA programming and C programming. Some of the following are listed below.
-
In C programming we use general functions to perform particular tasks where as in CUDA programming global specifier function is used that runs on device (GPU). It is generally invoked via host code, for example the main function in the above example, and is called as “kernel”.
-
When a kernel is invoked, its execution is provided via
<<<1,1>>>(variables)also called kernel launch.
Workflow in CUDA Programs
- Allocate memory to host and initialize the data of the host.
- Allocate memory to the device.
- Transfer the input data from host memory to device memory.
- Invoke or execute the kernel.
- Transfer the output from device memory to host memory.
Understanding CUDA programming with a sample code on Google Cloud
-
Open a new file in Google Colab and change the runtime to “GPU”.
- Uninstall any previous versions of CUDA, if any completely using below commands.
!apt-get --purge remove cuda nvidia* libnvidia-* !dpkg -l | grep cuda- | awk '{print $2}' | xargs -n1 dpkg --purge !apt-get remove cuda-* !apt autoremove !apt-get update - Install CUDA 9.0/10.0
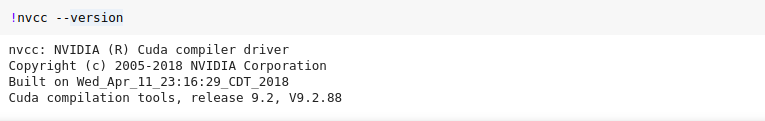
!wget https://developer.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/9.2/Prod/local_installers/cuda-repo-ubuntu1604-9-2-local_9.2.88-1_amd64 -O cuda-repo-ubuntu1604-9-2-local_9.2.88-1_amd64.deb !dpkg -i cuda-repo-ubuntu1604-9-2-local_9.2.88-1_amd64.deb !apt-key add /var/cuda-repo-9-2-local/7fa2af80.pub !apt-get update !apt-get install cuda-9.2 - Check version of CUDA installed with the following command:
!nvcc --version
The shell result would look like as follows:
Installation and Code snippet
- Execute the given command to install a small extension to run nvcc from Google Colab notebook cells.
!pip install git+git://github.com/andreinechaev/nvcc4jupyter.git - Load the extension using the following command:
%load_ext nvcc_plugin -
Now we will look on a simple CUDA code to understand the workflow.
3.1) To run CUDA C/C++ code in google colab notebook, add the %%cu extension at the beginning of your code.

3.2) global function device (GPU) to execute the multiplication of two variables.
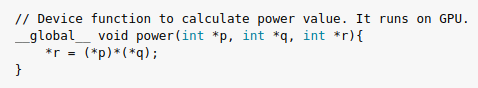
3.3) Declare variables for host and device.

3.4) Allocate memory for device variables and define variable values.

3.5) Copy input variables from host to device.
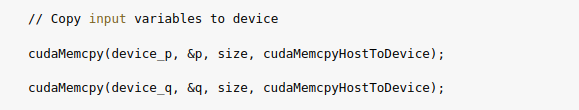
3.6) Launch the kernelto carry out the operations.
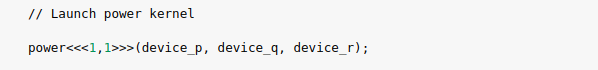
3.7) Copy the result back from device to host.
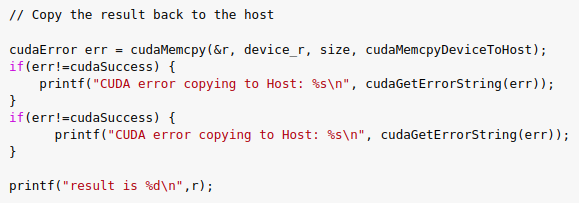
3.8) Free up the memory.

Advantages of CUDA Programming:
-
CUDA is majorly parallel hardware designed to run generic (non-graphic) code, with appropriate drivers for doing so.
-
CUDA is programming language based on C for programming and an assembly language that other programming languages can use as a target.
-
A software development kit that includes libraries, various debugging, profiling and compiling tools, and bindings that let CPU-side programming languages invoke GPU-side code.
-
The point of CUDA is to make us enable to write compatible massive parallel codes for SIMD architectures.
We will learn more about CUDA programming in the next blog post. The full code of the above is available at CUDA Programming PART1. Share your feedback and kindly reach out for any queries.
References:
`
