Paper Review on EfficientNet
In this blog post we will be focusing on the working of EfficientNet. We have seen that how CNN can be used for so many different tasks. Also we know that, once we increase the depth of CNNs they can detect the high level features more easily and with greater accuracy. But increasing the depth (adding more layers to CNN) has some major problems:-
-
Deeper networks are more difficult to train due to the vanishing gradient problem. Although several techniques, such as skip connections and batch normalization alleviate the training problem, the accuracy gain of very deep network diminishes.
-
Observations suggest that even for incresing the layers, a saturation point comes after which the accuracy saturates and it does not increase further, and then the other parameters get affected like FLOPS, fps etc.
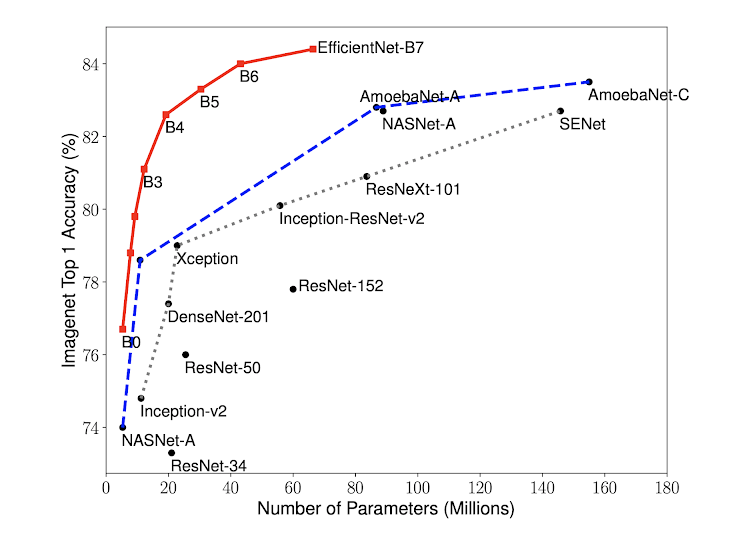
Also, we know that increasing the depth (number of layers) in CNN increases the number of parameteres by a large amount.The image below shows the comparison of number of parameters on ImageNet by different networks and EfficientNet.
In particular, the main question is if there is a principled method to scale upConvNets that can achieve better accuracy and efficiency? Study shows that it is critical to balance all dimensions of network width/depth/resolution, and surprisingly such balance can be achieved by simply scaling each of them with constant ratio. Based on this observation, a simple yet effective compound scaling method is proposed. Unlike conventional practice that arbitrary scales these factors, this method uniformly scales network width, depth, and resolution with a set of fixed scaling coefficients.
It still remains an open question of how to effectively scale a ConvNet to achieve better efficiency and accuracy. This paper work systematically and empirically studies ConvNet scaling for all three dimensions of network width, depth, and resolutions.
What are scaling methods?
1. Conventional scaling methods:- These methods mainly focus on increasing one dimension of network i.e, either width, depth, or resolution and the try to have a balance between the efficiency and accuracy.
2. Compound scaling methods:- These methods focus on increasing all the dimensions of the network i.e width, depth and resolution in a proportionate manner in order to keep a balance and improve the performance of the network.
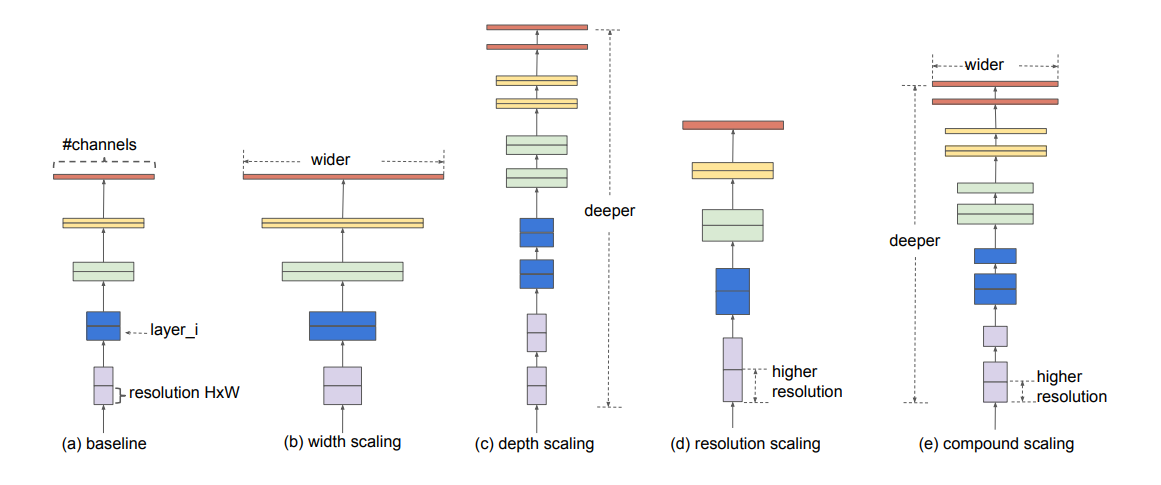
The above image (a)shows the baseline architecture, (b) width scaling, (c) depth scaling, (d) resolution scaling, (e) compound scaling.
Scaling Dimensions
Conventional methods mostly scale ConvNets in one of these dimensions i.e either depth wise, width wise or resoulution wise.
1. Depth wise scaling(d): Scaling network depth is the most common way used by many ConvNets. The intuition is that deeper ConvNet can capture richer and more complex features, and generalize well on new tasks. However, deeper networks are also more difficult to train due to the vanishing gradient problem. Although several techniques, such as skip connections and batch normalization alleviate the training problem, the accuracy gain of very deep network diminishes for example, ResNet-1000 has similar accuracy as ResNet-101 even though it has much more layers.
2. Width wise scaling(w): We find that wider networks tend to be able to capture more fine-grained features and are easier to train. However, extremely wide but shallow networks tend to have difficulties in capturing higher level features. Results show that the accuracy quickly saturates when networks become much wider with larger w.
3. Resolution wise scaling(r): Wider networks tend to be able to capture more fine-grained and high level features and are easier to train. However, extremely wide but shallow networks tend to have difficulties in capturing higher level features. The accuracy quickly saturates when networks become much wider with larger w.
Higher resolutions, such as 600x600, are also widely used in object detection ConvNets indeed higher resolutions improve accuracy, but the accuracy gain diminishes for very high resolutions.
From the experiments, two conclusions can be drawn:-
Conclusion
- Scaling up any dimension of network width, depth, or resolution improves accuracy, but the accuracy gain diminishes for bigger models.
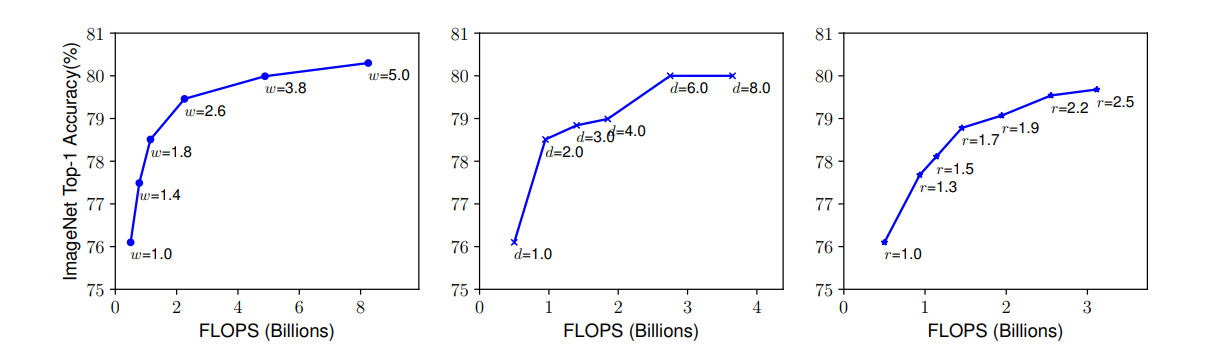
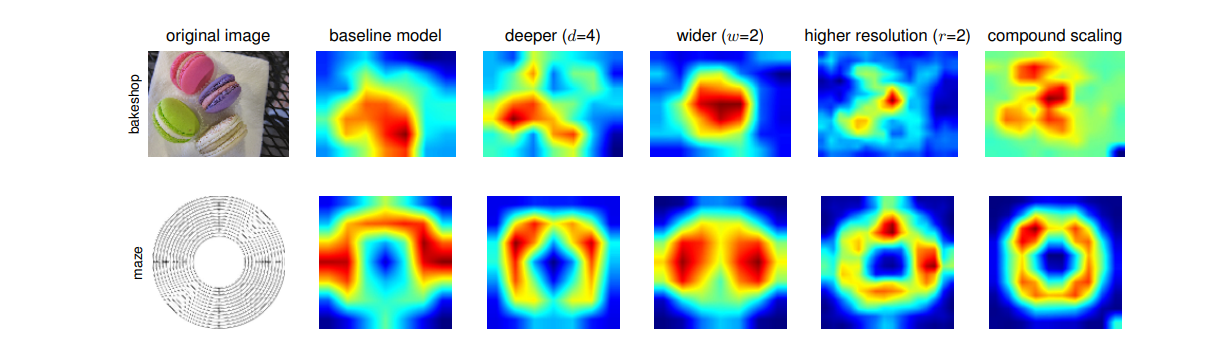
The above image shows scaling Up a Baseline Model with Different Network Width (w), Depth (d), and Resolution (r) Coefficients. From the above, we can observe that all the models saturate in terms of accuracy when scaling is applied in only one dimension.
- In order to pursue better accuracy and efficiency, it is critical to balance all dimensions of network width, depth, and resolution during ConvNet scaling.
Working Architecture of EffcientNet:
They use compund scaling in which they use a compound coefficient φ to uniformly scale network width, depth, and resolution in a principled way where α, β, γ are constants that can be determined by a small grid search.
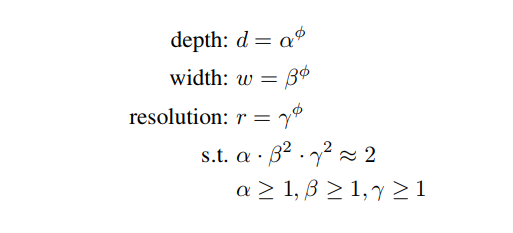
φ is a user-specified coefficient that controls how many more resources are available for model scaling, while α, β, γ specify how to assign these extra resources to network width, depth, and resolution respectively.
References
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1905.11946.pdf
- https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Birdsnap%3A-Large-Scale-Fine-Grained-Visual-of-Birds-Berg-Liu/4965eec4d6fd69e9bff12dce7d9d84897433cc2a.
